|
男性性生理问题
|
|
隐睾症
医学术语:隐睾症(Cryptorchidism
)(自希腊语“kryptos:隐藏的”+“orchis:睾丸”)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
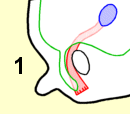
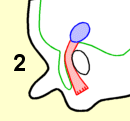
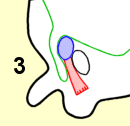
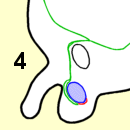
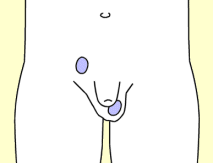
当男胎在子宫内发育的时候,他的睾丸会逐渐降入发育中的阴囊。此处所示为在导向组织索的协助下正在降入阴囊的睾丸(兰色):
1.第二月;
2.第三月;
3.第七曰;
4.出生时。
As the fetus grows inside the womb, his testicles gradually descend into the developing scrotal sac. Shown here is a testicle (blue) descending with the help of a guiding cord (red) into the scrotum.
1 second month
2 third month
3 seventh month
4 at birth
|
|
|
|
|
|
当男胎在子宫内发育时,他的睾丸在其腹腔内生成,然后在临出生前不久,下降到阴囊。可是,在某些病例,睾丸未能下降,男婴仍带着未下降的睾丸出生了。新生男婴中,隐睾症的发生率约为4%,而早产儿中约有30%。只有一个睾丸未能下降也是可能的。在某些罕见的病例,已经下降到阴囊的睾丸又往上移到腹股沟区[所谓回撤睾丸(retractile testicle)]。通常,医生能够简单地从这个区域把睾丸复位。
在大多数的情况下,未下降的睾丸在出生后数月内会自动向下移入阴囊。可是,如果没有发生这种自动的复位,就需要去治疗了,因为,在腹膜腔内,睾丸暴露在常规的体温之下,这个体温对于正常产生精子温度过高。这将导致男性不育。隐睾症也有引起疝气的危险,甚或演变成睾丸肿瘤。
|
|
|
|
男婴:(左)双侧睾丸已经降入阴囊;(右)一侧睾丸没有下降而仍存留在腹膜腔。
Infant boys: (left) Both testicles have descended into the scrotum.
(right) One testicle has not descended but has remained inside the abdomen.
|
治
疗
隐睾症的常规治疗是外科手术。复位手术应该尽可能早地实施,也就是说,在出生后第3-18个月内进行。这将为避免往后的不育症提供了最好的时机。出身时带有隐睾症或因该症经过治疗的男孩当进入青春期时,应该被告知疾病真相,并且应该学会如何有规律地自我检查睾丸,以探测任何肿块以及由此所致的可能的早期睾丸癌的迹象。这种自我检查实际上被推荐给所有的男子(见睾丸自查)。至于成年男子,睾丸外科手术复位并由此而想恢复生育能力通常是太迟了。代替复位手术的,可能单纯地切除睾丸。通常,对超过40岁的隐睾症男性患者根本不再进行任何治疗了。
|
|
Physical Problems in Males
Undescended Testicles
Medical term:
Cryptorchidism (gr. kryptos: “hidden” + orchis: “testicle”)
As a male fetus grows inside his mother's womb, his testicles form inside his abdomen and then, shortly before birth, descend into the scrotum. However, in some cases, this fails to happen and the infant boy is born with still
undescended testicles. The condition is found in about 4% of newborn boys and in about 30% of boys born prematurely. It is also possible that only one of the two testicles fails to descend. In some rare cases, a testicle that has already descended into the scrotum moves up again into the groin area (a so-called
retractile testicle). Usually, the doctor can simply retract it from there.
In
most cases, undescended testicles move
down into the scrotal sac on their own
within the first few months.
However, if this does not happen,
treatment becomes necessary, because
inside the abdomen the testicles are
exposed to normal body temperature which
is too high for normal sperm production.
This could lead to infertility. There is
also some danger of a hernia or even a
tumor developing.
|
|
Treatment
The usual treatment of undescended testicles is surgery. It should be performed as soon as possible, i.e. between the 3rd and 18th month after birth. This offers the best chance of avoiding later infertility. Males born with and treated for undescended testicles should be told about it when they reach puberty, and they should learn how to do a regular self-exam of their testicles in order to detect any lumps and thus possible early signs of testicluar cancer. Such self-exams are actually recommened for all males (see
Testicular self-examination). For adult males, it is usually too late to move undescended testicles into the scrotum and thus to restore fertility. Instead, the testicles may simply be surgically removed. As a rule, men over 40 no longer receive any treatment for this condition at all.
|