|
男性性生理问题
|
|
睾丸鞘膜积液
|
|
睾丸鞘膜积液(自希腊语:hydor-“水”+kele:“破裂”或“空洞、窦腔”)是指环绕睾丸周围的液体统称。该症状在婴儿不是不常见,可是在成人却罕见。最通常的情形是,睾丸鞘膜积液只出现在一侧,发生在两侧的病例只有10%。
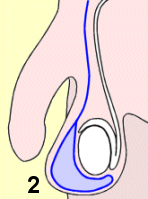
大多数睾丸鞘膜积液是先天的,也就是说,男婴生下来就带有积液。其病因是:当睾丸在出生之前降入阴囊时,鞘膜囊和来自于腹腔内部的液体往下流向阴囊。这个鞘膜囊通常是封闭的,而液体会被吸收。可是,如果液体不能够往上流回腹膜腔,而是仍留在这个封闭的鞘膜囊内,就会导致所谓的非交通性睾丸鞘膜积液(non-communicating
hydrocele)。这种症状通常在出生后的18个月内自行消失。
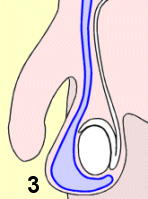
在某些病例,这个鞘膜囊本身仍然开放,而液体能够在阴囊和腹膜腔之间上下流动。这种病例,医学上称作交通性睾丸鞘膜积液(communicating
hydrocele)。在夜间休息之后它会变小,在白天活动后,则会变大。
|
|
|
|
|
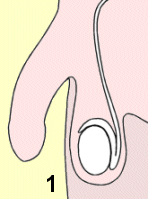
1
正常阴囊 2
非交通性睾丸鞘膜积液
3
交通性睾丸鞘膜积液
1 Normal scrotum 2 non-communicating hydrocele 3 communicating hydrocele
|
|
治
疗
未产生症状的少量睾丸鞘膜积液不需要治疗。但是,如果产生不适或因其尺寸过于引人注目,则预示着需要医学治疗。成人的睾丸鞘膜积液可能预示着身体内部的某种损伤或严重的潜在疾病。所以,总是需要做彻底的身体检查和细致的诊断,以排除其他的病症。其他的两个(需要鉴别诊断的)病症可能是疝气(hernia)和睾丸扭转(testicular
torsion )。18个月大的婴儿明显的睾丸鞘膜积液可能也需要医学治疗。经常的情形是,随着时间推移,睾丸鞘膜积液有增大的倾向。最常见的治疗是外科手术,有时合并使用针管抽液和药物注射。
|
|
Physical Problems in Males
|
|
Hydrocele
|
|
A hydrocele (from gr. hydor: “water” + kele: “break” or “cavity”) is a collection of fluid around the testicle. The condition is not uncommon in newborns, but rare in adults. Most often, a hydrocele appears only on one side. Hydroceles on both sides occur in only about 10% of the cases.
In most cases, a hydrocele is congenital, i.e. a baby boy is born with it. The cause is this: When the testicles descend into the scrotum before birth, a sac and some fluid from inside the abdomen move down along with it. The sac usually closes, and the fluid is absorbed. However, if it cannot flow back upward and remains inside the closed sac, it produces a so-called
non-communicating hydrocele. This condition usually corrects itself within the first 18 months of life.
In some cases, the sac itself remains open, and the fluid can travel up and down between scrotum and abdomen. In this case, one speaks of a
communicating hydrocele. It is smaller after a night’s rest and larger after a day of activity.
Treatment
A small hydrocele that produces no symptoms does not require treatment. However, if it produces discomfort or becomes too noticeable because of its size, medical treatment may be indicated. A hydrocele appearing in an adult may indicate some internal injury or serious underlying disease. Therefore, a thorough examination and careful diagnosis - ruling out other problems - are always necessary. Two of these other problems may be a hernia or
testicular torsion (see there). An obvious hydrocele in an infant boy older than 18 months may also require medical attention. Very often, hydroceles tend to get larger over time. The most common treatment is surgery, sometimes combined with needle aspiration and the injection of some medication.
|