|
男性性生理問題 |
|
精液囊腫
|
|
|
|
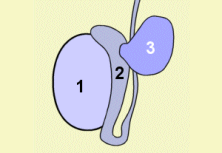
1:睾丸;2:附睾;3:精索囊腫
1: Testicle 2: Epididymis
3: Spermatocele
|
|
|
|
|
精液囊腫(自希臘語spermatos:“精子”+kele:“破裂或竇腔”)是一種在精索內一處或數處含有液體的良性包囊或膨脹物。液體內含有精子(故此而得名)。精液囊腫通常位於附睾的頭部,其次位於睾丸的頂端。囊腫可能非常小,也可能相當大而引人注目,並且可以只發生在一側或兩側都有。精液囊腫可能導致不適或疼痛,或者根本就感知不到。可是,這種病症不是不常見的,而許多病人沒有任何症狀,因而未能覺察。精液囊腫的病因未明。
治
療
單純的精液囊腫如果較小勿需治療。甚至較大,只要沒有什麼症狀,也勿需治療。但是,如果它持續變大或導致疼痛,則預示著可能需要醫學介入。治療涉及到外科手術摘除(“精液囊腫切除術,spermatocelectomy”)。
|
|
|
|
Physical Problems in Males |
|
Spermatocele
|
|
A spermatocele (from gr. spermatos: “sperm” + kele: “break or cavity”) is a benign cyst or distension with fluid of the spermatic cord in one or several places. The fluid contains sperm (thus the name). Spermatoceles are usually found at the head of the epididemis, next to the top of the testicle. They may be very small or rather large and noticeable, and they may occur on only one or on both sides. They may cause some discomfort or pain, or they may not be felt at all. Indeed, the condition is not uncommon, but many men have no symptoms and thus are not aware of it. The causes are unknown.
Treatment
A simple, small spermatocele does not require treatment.This remains true even if it is larger, but asymptomatic. However, if it continues to enlarge or causes pain, some medical intervention may be indicated. This may involve the surgical removal of the spermatocele (“spermatocelectomy”).
|