|
中間性
-
中間性性象譜 |
|
中間性的原因
-
染色體因素
|
|
女性:特納氏綜合征
(Turner Syndrome)
(也叫阿爾瑞契-特納氏綜合征,Ullrich-Turner
Syndrome;單體X性染色體, Monosomy
X)
|
|
術語“綜合征(syndrome)”是指具有相同病因的一系列病症的統稱。在這種病例,綜合征是以美國內科醫生亨利•特納(Henry Turner)的名字命名的,他於1930年代描述了該病的一些特徵[在中國大陸醫學界,該綜合征被稱為先天性卵巢發育不全症(congenital
ovary dysgenesis)、或性腺發育不全症(congenital
dysgenesis)、或XO-Turner綜合征(The
XO Turner Syndrome),為了記憶方便,筆者此處按照首位描述該病的特納先生的姓翻譯成“特納氏綜合征”——譯者注]。在每一個這樣的病例中,不僅可能存在著各種各樣的症狀,而且這些症狀源自相同的病因:只有單一的X染色體,而不是正常的兩條X染色體(XX)。第二條X染色體丟失了(X0)。缺乏第二條X染色體的原因尚未可知,這似乎是一個隨機發生的事件。罹患特納氏綜合征的女性可能具有下述插圖例舉的幾個、許多或全部的生理特徵:
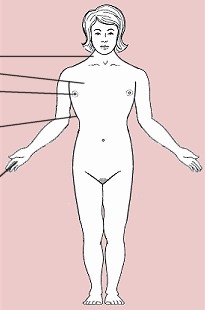
罹患特納氏征合征者的可能生理特徵
Possible physical features related to Turner syndrome
|
|
|
外表特徵異常
身材矮小
蹼頸
寬胸
乳頭相距遠
可能有脊柱彎曲(脊柱側凸)
肘外翻
短指
(嬰兒期)手和足背水腫
|
|
|
|
|
內部結構或功能異常
卵巢發育不全
不孕
閉經
可能出現的症狀:
心血管症狀(主動脈狹窄多見)
高血壓
聽力障礙
近視
智商低於常規水準
甲狀腺功能障礙
腎臟功能障礙
糖尿病
骨質疏鬆 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intersexuality - The Intersexual Spectrum |
|
Causes of Intersexuality - Chromosomes
|
|
Females: Turner Syndrome (also called Ullrich-Turner Syndrome, Monosomy X)
|
|
The term “syndrome” refers to a variety of symptoms that have the same cause. In this case, the syndrome is named after the American physician
Henry Turner who described some of its features in the 1930s.
Not all possible symptoms are present in each case, but they do have the same cause: Instead of the typical two X– chromosomes (XX), there is only a single X-chromosome. The second one is missing (X0). The reason for this is unknown. The absence of a second X-chromosome seems to be a random event. Females with Turner syndrome may have some, many or all the the physical features summarized in the following illustration: Possible physical features related to Turner syndrome
|
|
|
External
short stature
extra skin on the neck
wide chest
breast nipples far apart
possible curvature of
the spine (scoliosis)
arms that turn out
slightly at the elbow
short fingers
puffy hands and feet
|
|
|
|

|
Internal
undeveloped ovaries
infertility
no menstruation
Possible problems:
heart problems
high blood pressure
ear and hearing problems
shortsightedness
learning difficulties
thyroid problems
kidney problems
diabetes
osteoporosis
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|