|
Intersexuality - The Intersexual Spectrum
|
|
Causes of Intersexuality - Chromosomes
|
|
Females: Turner Syndrome (also called Ullrich-Turner Syndrome, Monosomy X)
|
|
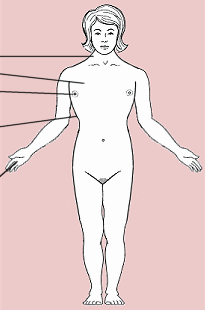
The term “syndrome” refers to a variety of symptoms that have the same cause. In this case, the syndrome is named after the American physician Henry Turner who described some of its features in the 1930s. Not all possible symptoms are present in each case, but they do have the same cause: Instead of the typical two sex chromosomes (XX or XY), there is only a single X-chromosome while the second one is missing. In shorthand, this condition is called X0. The reason for this is unknown. The absence of a second X-chromosome seems to be a random event. Females with Turner syndrome may have some, many or all the the physical features summarized in the following illustration:
Possible physical features related to Turner syndrome
|
|
|
|
|
External
short stature
extra skin on the neck
wide chest
breast nipples far apart
possible curvature of
the spine (scoliosis)
arms that turn out
slightly at the elbow
short fingers
puffy hands and feet
|
|
|
|
|
|
Internal
undeveloped ovaries
infertility
no menstruation
Possible problems:
heart problems
high blood pressure
ear and hearing problems
shortsightedness
learning difficulties
thyroid problems
kidney problems
diabetes
osteoporosis
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
.
|