性-人類性的基本層面
Sex
- Basic Aspects of Human Sexuality |
|
染色體的功能:染色體如何決定一個人的性? |
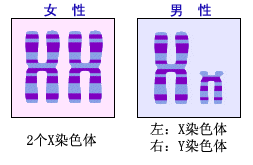 人體細胞含46條染色體,其中的2條決定著一個人的性:女性有兩條X染色體(44+XX);男性有一條X染色體和一條Y染色體(44+XY)。然而,卵細胞在成熟和準備受精之前,她減少了一半的染色體(結果是:22+X)。同樣的,精子在達到完全成熟之前,他也只有一半的染色體(結果是:22+X或22+Y)。在受/授精期間,保留那一半染色體的卵子和精子發生融合,形成一個新的完整細胞。所以,這個新細胞可能含有44+XX或44+XY染色體。因此,新細胞將會要麼發育成女性個體,要麼發育成男性個體。但是,在胚胎早期,我們在外觀上區分不了男女個體。 人體細胞含46條染色體,其中的2條決定著一個人的性:女性有兩條X染色體(44+XX);男性有一條X染色體和一條Y染色體(44+XY)。然而,卵細胞在成熟和準備受精之前,她減少了一半的染色體(結果是:22+X)。同樣的,精子在達到完全成熟之前,他也只有一半的染色體(結果是:22+X或22+Y)。在受/授精期間,保留那一半染色體的卵子和精子發生融合,形成一個新的完整細胞。所以,這個新細胞可能含有44+XX或44+XY染色體。因此,新細胞將會要麼發育成女性個體,要麼發育成男性個體。但是,在胚胎早期,我們在外觀上區分不了男女個體。 |
The Role of Chromosomes:
How do the chromosomes determine a person's sex? |
|
Human body cells contain 46 chromosomes, of which 2 determine a person's sex: In the female body they are two X-chromosomes (44+XX), in the male body they are one X-chromosome and one Y-chromosome (44+XY). However, before an egg cell matures and becomes ready for fertilization, it loses half of its chromosomes (result: 22+X). Similarly, before it reaches its full maturity, a sperm cell loses half its chromosomes (result: either 22+X or 22+Y). During fertilization the two remaining halves unite to form a new complete cell. Thus, the new cell may have either 44+XX or 44+XY chromosomes. Accordingly, it will develop in the direction of either a female or male individual. However, at the embryonic stage, the two are still outwardly indistinguishable. |

